Capital structure is a complex area of financial decision making due to the relationship between the firm's financing sources, the firm's risk/return profile, and the firm’s value
External Assessment of Capital Structure
Debt Ratios can be used to measure the firm's degree of financial leverage
Measurements of indebtedness
Measurements of ability to service debt
The more risk a firm is willing to take, the greater will be its financial leverage
A firm should theoretically maintain a level of financial leverage consistent with the capital structure that maximizes shareholder wealth
There are significant differences in typical degrees of financial leverage between industries
Capital structure patterns among industries tend to be quite similar around the world
Capital Structure Theory
How a chosen financing mix affects the firm's value has been a topic of considerable study
Modigliani and Miller (hereafter "M & M") demonstrated algebraically that, assuming perfect markets, capital structure has no effect on the firm's value
The major costs of debt financing include
The probability of bankruptcy due to an inability to meet obligations depends on:
Business Risk
Financial Risk
Agency Costs Imposed by Lenders
Asymmetric Information
Asymmetric Information
If a firm's managers feel that the firm's stock is undervalued and there is an available investment that they feel will increase the value of the firm, the managers will use debt financing to fund it
If a firm's managers feel that the firm's stock is overvalued, however, they will use a stock issue to finance the investment
Debt is generally seen as a positive signal
Equity is generally seen as a negative signal
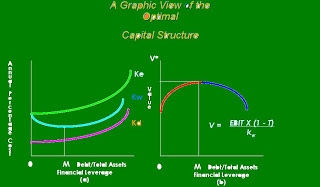
Cost Functions
kd = After-tax cost of debt
ke = Cost of equity
kw = Weighted average cost of capital
The cost function graphs illustrate the behavior of the costs of debt and equity as their use increases by the firm. Their combined effect on the weighted average cost of capital is also shown.
A Graphic View of the Optimal Capital Structure



No comments:
Post a Comment